In its efforts to bring the many benefits of additive manufacturing (AM) to the global marketplace, Immensa Technology Labs has established offices in five different countries and spearheaded some of the most exciting CD printing projects in the world. But before it can provide high quality AM services to its ever-expanding client base, Immensa must typically sell prospective customers on the value of AM in general.
Across a broad scope of industries and market sectors, far too many organizations are failing to leverage the many advantages that additive manufacturing presents. This is unsurprising because AM takes a whole new approach to the very fundamentals of manufacturing.
When it comes to individual parts and components, many traditional manufacturing techniques involve subtractive processes. In other words, machinists generally carve or cut parts out of a block of solid metal or another raw material.
How Additive Manufacturing Works
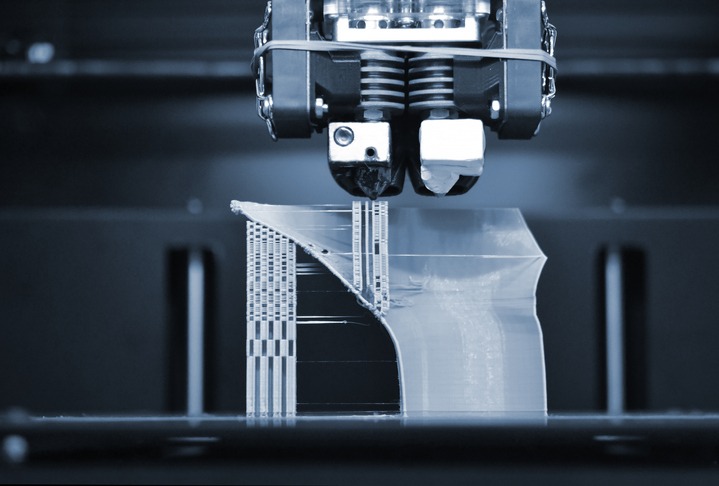
The AM approach turns the subtractive manufacturing (SM) approach upside down, creating solid forms by building something up rather that tearing something down. One of the benefits of AM as compared with SM should be immediately evident. Because it begins with nothing and then adds material, AM is far less wasteful than SM, which begins with a block of material and then generates unwanted scraps.
While injection molding and a few other well-established manufacturing processes technically qualify as AM, the term is more widely used to describe modern 3D printing processes. 3D printing equipment and software are capable of producing any number of component parts and other items by adding metal, plastic, or another raw material, layer after layer, until the desired final form is achieved. AM has a proven ability to fabricate a virtually unlimited assortment of products with an incredibly high degree of precision.
Operating with robotic efficiency and digitally guided by a CAD (computer-aided design) model, the 3D printer gradually adds material to create solid forms to perform a wide array of specific functions and meet a wide array of specific needs. The global engineering membership organization TWI lists a spectrum of distinct AM processes in common use, ranging from binder jetting and direct energy deposition to vat polymerisation and powder bed fusion.
How Immensa Leverages AM Technology to Offer Business Solutions
With offices in Dammam, Saudi Arabia, Dubai, United Arab Emirates; Kuwait City, Kuwait; Amman, Jordan; and Houston, Texas; Immensa Technology Labs is an international leader in the AM field. The company maintains a particular focus on changing the way companies around the world physically access the spare parts that they need to keep business in motion.
In short, Immensa technology enables companies to print whatever spare parts they need on-site. Stressing sustainability, efficiency, and financial viability, Immensa leverages the power of AM and associated advanced technologies to “take physical spare parts and dematerialize them into the digital, on-demand world.” This allows companies to produce a limitless number of spare parts from a virtual warehouse that requires no physical space whatsoever.
Any company that has been forced to halt operations because they can’t replace a failed component part knows just how costly this kind of wait can be. Immensa’s manufacturing as a service (MaaS) prevents these potentially devastating setbacks by eliminating the need to order, ship, and receive parts in the mail. With a global supply chain that has remained in shambles since the onset of the COVID-19 pandemic in 2020, the ability to print spare parts on-site is an attractive benefit indeed!
Immensa’s accomplished team of AM professionals take MaaS clients through every step of the AM process from initial concept to post-processing. They have specific expertise in areas that range from material qualification to model simulation to parameter optimization.