In the landscape of ancient inventions, Ctesibius’ Water Clock, known as the Clepsydra, stands as a testament to the ingenuity of early engineering. Ctesibius, a Greek inventor and mathematician from Alexandria, Egypt, revolutionized timekeeping in the 3rd century BC with his sophisticated design of the water clock. This device was not only a functional tool for measuring time but also a marvel of mechanical complexity and precision.
In an era long before the advent of modern clocks, the Clepsydra represented a major advancement in technology, offering a more accurate and consistent method of timekeeping than its predecessors. The water clock’s design reflected Ctesibius’ mastery of hydraulics and pneumatics, disciplines he is credited with founding. This article explores the intricate workings and historical significance of Ctesibius’ Water Clock to discover how Ctesibius’ Water Clock played a crucial role in the evolution of timekeeping devices.
What is Ctesibius’ Water Clock?
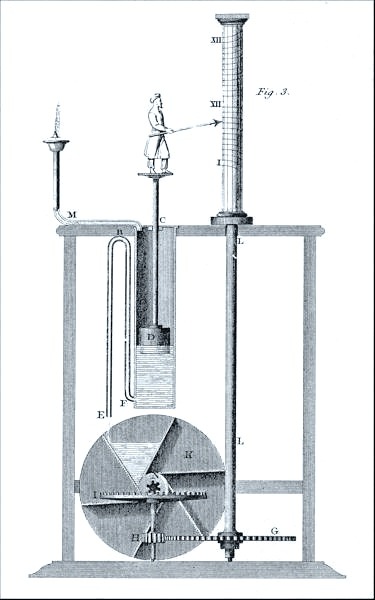
Ctesibius’ Water Clock, or Clepsydra, was a remarkable achievement in the ancient world, representing a significant leap forward in timekeeping technology. Invented in the 3rd century BC, this device was a sophisticated apparatus that used water to measure time more accurately than previous methods.
The Basic Mechanism
At its core, the Water Clock was relatively simple. It consisted of a container filled with water, which would slowly drip out through a small hole at the bottom. As the water level decreased, the passage of time could be measured. However, Ctesibius took this basic principle and enhanced it dramatically, turning the Water Clock into a complex and reliable instrument.
Innovations by Ctesibius
Ctesibius introduced several key innovations that set his Water Clock apart. He incorporated a float and indicator system into the design. As water dripped out of the main container, it filled a secondary vessel where a float rose with the water level. This float was connected to a pointer or a series of gears that moved a dial or a display, showing the passage of time in a visual and more readable manner.
Regulating the Flow
One of the most significant challenges with early water clocks was the variable flow rate due to changing water pressure as the container emptied. Ctesibius addressed this by adding a constant-flow regulating system, possibly using an inflow water tank with an overflow mechanism. This innovation ensured that the rate of water flow remained consistent, leading to more accurate time measurements.
Impact on Timekeeping
Ctesibius’ Water Clock was a marvel of its time, combining principles of hydraulics and mechanics. It allowed for a more precise division of hours and minutes than earlier sundials or simpler water clocks. The Clepsydra became a vital instrument in various aspects of ancient life, from public timekeeping to timing in legal proceedings.
The mechanics and principles used in the Water Clock laid the groundwork for later developments in mechanical clocks. The use of gears and escapements, crucial components in modern clockwork, can trace their conceptual origins back to the innovations introduced by Ctesibius. His work with gears and water regulation inspired future clockmakers to experiment with mechanisms that could control the movement of a clock’s hands with precision.
Who Was Ctesibius?
Ctesibius, often hailed as the father of pneumatics, was an eminent Greek inventor and mathematician in Alexandria, Egypt, around the 3rd century BC. His contributions to the fields of engineering and science are considered groundbreaking, laying the foundation for many modern technologies. Ancient Alexandria is one of the biggest cities during the ancient times. If you are interested to find out the other cities that made it on the list, you may read our article, What Were the Largest Cities in the Ancient World and What Secrets Do They Hold?
Early Life and Background
Though details about Ctesibius’ early life are sparse, historical accounts suggest he was born in Alexandria, a city renowned for its cultural and intellectual vitality. He likely spent most of his life in this hub of learning and innovation, which at the time was home to the famous Library of Alexandria.
Contributions to Science and Engineering
Ctesibius’ most notable contributions lie in the fields of pneumatics and hydraulics. He is credited with several inventions that demonstrate his deep understanding of air and water pressure. His works include the water clock, or Clepsydra, which significantly improved the accuracy of time measurement, and a water organ, which showcased the principles of air pressure in creating music.
The Father of Pneumatics
Ctesibius’ experiments and inventions in pneumatics were pioneering. He was among the first to study the properties of compressed air and its potential for use in devices like pumps and engines. His work in this field established the basic principles of pneumatics that are still studied and applied in modern technology.
The Legacy of Ctesibius
Ctesibius’ legacy as an inventor and scientist is significant. His innovative spirit and contributions to understanding fluid dynamics and air pressure mechanics have earned him a lasting place in the history of science. Many of his inventions and discoveries were far ahead of their time, reflecting a level of ingenuity and foresight that was remarkable for his era.
Conclusion
Through his ingenious use of water and mechanics, Ctesibius of Alexandria managed to transform the way time was measured, moving away from the erratic methods of the past to a more reliable and systematic approach. His invention was more than just a device to mark the hours; it was a symbol of human ingenuity and the quest for precision and order.
The legacy of Ctesibius’ Water Clock extends far beyond its immediate functionality. It laid the groundwork for the development of more advanced timekeeping devices, including mechanical clocks, and it influenced various fields, from horology to physics. The principles he employed in the creation of the Clepsydra echo through time, continuing to inform and inspire modern technology.