The Industrial Revolution, a period of profound change in manufacturing, transportation, and technology, saw the birth of many innovations that radically transformed industries. One such invention was the Spinning Mule, a machine that played a crucial role in advancing textile production.
The Invention of the Spinning Mule
The Spinning Mule was invented in 1779 by Samuel Crompton, an English inventor and pioneer in the spinning industry. Crompton, who had a background in textile work, sought to improve upon the existing technology of the time, namely the Spinning Jenny and the Water Frame. The Spinning Mule combined features of both these machines, offering greater control over the spinning process and producing a finer, stronger thread.
Crompton was born to a family with a background in textile work. His early years were marked by a combination of agricultural work and spinning. The Crompton family spun yarn for local textile manufacturers using spinning wheels at home, a common practice in rural England at that time.
The critical achievement of Samuel Crompton’s life was his invention of the Spinning Mule in 1779. Crompton developed this machine due to the limitations of existing spinning technology, namely the Spinning Jenny and the Water Frame. The Spinning Mule combined the best features of both these machines, allowing for the production of a finer, stronger thread. It could spin cotton thread suitable for use in the manufacture of muslin, a very fine and valuable fabric at the time. This invention was crucial in advancing the British textile industry during the Industrial Revolution.
How the Spinning Mule Works
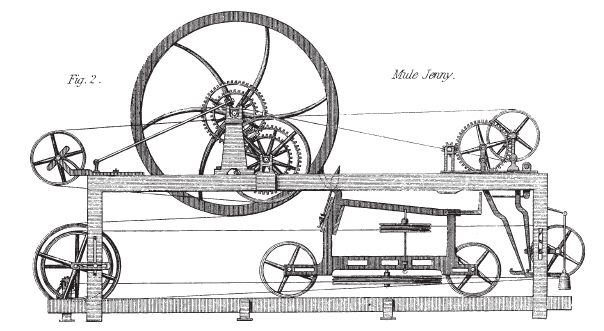
The genius of the Spinning Mule lay in its intricate mechanism. The machine was named a ‘mule’ because it combined aspects of its two predecessors just as a mule is a cross between a horse and a donkey. Over time, the design of the Spinning Mule was refined, and it became capable of housing hundreds of spindles, significantly increasing productivity.
The mechanism of the Spinning Mule is a fascinating example of industrial engineering and design, combining the principles of both the Spinning Jenny and the Water Frame. Here’s an expanded look at how the Spinning Mule operates:
Basic Operation – The Spinning Mule functioned through a series of coordinated movements to spin cotton or wool fibers into yarn. The machine had two main components: a fixed part, which held the rovings (the unspun fibers), and a moving carriage, which carried the spindles.
Drawing and Twisting – As the carriage moved away from the fixed frame, it drew out the fibers. This process involved gently pulling the fibers so they became longer and thinner. Once the carriage reached a certain distance, the spinning process began. Here, the spindles, which were part of the carriage, twisted the fibers into yarn. The twisting was crucial as it gave the yarn strength and cohesion.
Setting the Twist – As the carriage returned to its original position, the newly spun yarn was wound onto the spindles. This movement effectively set the twist in the yarn, ensuring it wouldn’t unravel. The distance of the carriage’s travel and the speed of the spindles could be adjusted depending on the desired thickness and strength of the yarn.
Complexity and Refinement – The Spinning Mule’s complexity allowed for precise control over the spinning process. The mule could be operated manually or powered by water or steam engines in larger installations. Over time, the design was refined to increase the number of spindles, allowing one mule to produce multiple threads simultaneously, vastly increasing productivity.
Improved Yarn Quality – The Spinning Mule was particularly noted for its ability to produce fine, strong yarn. The controlled drawing and twisting, combined with the ability to adjust the spindle speed and carriage distance, allowed for a high degree of precision. This precision resulted in yarn that was uniform in thickness and strength, suitable for weaving into high-quality fabrics.
Automation and Labor – Initially, the Spinning Mule was semi-automated, requiring skilled labor to operate. However, as technology advanced, more automated versions were developed. This evolution marked a shift from skilled artisanal labor to more unskilled labor in the textile industry.
The Spinning Mule’s design and operation were pivotal in advancing textile manufacturing during the Industrial Revolution. Its ability to produce high-quality yarn in large quantities not only revolutionized the textile industry but also had far-reaching economic and social impacts, contributing to the rise of factory-based production and the decline of home-based textile craft.
Impact on the Textile Industry
The introduction of the Spinning Mule marked a turning point in the textile industry. Its ability to produce fine, strong yarn at a much faster rate than previous spinning methods led to a significant increase in cloth production, meeting the growing demand for textiles during the Industrial Revolution.
The Spinning Mule was instrumental in the growth of the cotton industry, particularly in Great Britain, which became the global center of cotton production. It facilitated the shift from home-based manual spinning to factory-based mechanized production. This transition not only boosted output but also changed the nature of labor, leading to the growth of factory towns and the expansion of the industrial workforce.
While the Spinning Mule itself is not used in production anymore, its influence is still evident. It marked a significant advancement in textile manufacturing, laying the groundwork for future innovations in the industry. The principles of drawing and twisting fibers into yarn, which were so effectively combined in the Spinning Mule, remain fundamental to modern spinning processes.
Economic and Social Impact
The economic impact of the Spinning Mule was profound. It contributed significantly to the wealth of nations, particularly Great Britain, by enhancing the efficiency and scale of textile production. The machine’s efficiency and productivity laid the foundation for the modern textile industry, influencing global trade and economics.
However, the social impact was mixed. While the Spinning Mule played a role in creating jobs in new industrial centers, it also contributed to the decline of the traditional home-based textile industry. The shift to factory work led to changes in social structures, with a notable impact on the workforce, including women and children, who formed a significant part of the factory labor force.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the Spinning Mule was more than just a technological marvel of the Industrial Revolution; it was a catalyst for change. By revolutionizing textile manufacturing, it played a pivotal role in shaping the economic and social landscape of the era. Its legacy is seen in the modern textile industry, which continues to evolve with new technologies. Samuel Crompton’s invention epitomizes the innovative spirit of the Industrial Revolution, highlighting how a single invention can have far-reaching implications across various facets of society.