Attention to those seeking alternative treatments for ADD! In this comprehensive review, we delve into the effectiveness of Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS) as a potential solution. Whether you’re exploring alternative avenues for managing ADD symptoms or seeking more information on TMS, this article is your guide. Read on to uncover insights into this innovative treatment option.
Introduction
Attention Deficit Disorder (ADD), characterized by difficulty in sustaining attention, hyperactivity, and impulsivity, affects millions worldwide. While traditional treatments like medication and therapy are prevalent, many individuals seek alternative approaches due to concerns about side effects or lack of efficacy. This quest has led to the exploration of Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS), a non-invasive procedure that utilizes magnetic fields to stimulate specific areas of the brain.
Exploring TMS for ADD
Understanding TMS
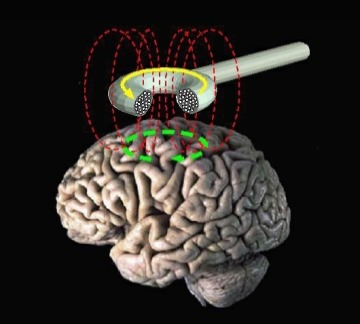
Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS) operates on a fascinating principle: harnessing electromagnetic pulses to specifically target areas of the brain linked to Attention Deficit Disorder (ADD) symptoms. This targeted approach stands in stark contrast to traditional medications, which often blanket the entire brain with their effects, leading to a plethora of potential side effects. With TMS, however, precision is paramount. By honing in on specific brain regions, TMS minimizes collateral damage and offers a promising avenue for reducing unwanted side effects.
At its core, TMS seeks to recalibrate neural activity within the brain circuits responsible for attention regulation. Through the precise application of electromagnetic pulses, TMS aims to restore balance to these intricate networks. Imagine it as a gentle tuning fork for the brain, fine-tuning neural pathways to promote more effective attention management. This nuanced approach holds immense potential for individuals grappling with the disruptive symptoms of ADD, offering hope for a more targeted and tailored treatment option.
Efficacy of TMS
The ongoing research exploring the effectiveness of Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS) for Attention Deficit Disorder (ADD) offers promising insights into its potential as a therapeutic intervention. Numerous studies have demonstrated encouraging results, with notable improvements observed in key areas such as attention, impulsivity, and hyperactivity among individuals undergoing TMS treatment sessions.
These findings highlight the transformative impact that TMS can have on the lives of those struggling with ADD symptoms. While it’s essential to acknowledge that individual responses to TMS may vary, the collective evidence suggests a tangible benefit for many patients. Reports of substantial symptom reduction and enhanced quality of life underscore the significance of TMS as a viable treatment option in the management of ADD.
As research continues to unfold, further elucidating the mechanisms underlying TMS efficacy and refining treatment protocols, the potential for even greater strides in addressing ADD symptoms grows. With each new study and clinical trial, the evidence supporting the effectiveness of TMS strengthens, offering renewed hope to individuals seeking relief from the challenges posed by ADD.
Safety and Side Effects
One of the standout advantages of Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS) as a treatment for Attention Deficit Disorder (ADD) lies in its remarkable safety profile, a feature that distinguishes it from conventional medication-based therapies. While medications often carry the risk of systemic side effects, affecting various bodily systems, TMS offers a more localized approach. By precisely targeting specific brain regions implicated in ADD symptoms, TMS minimizes the likelihood of adverse reactions occurring outside the intended treatment area.
This targeted modulation of neural activity not only enhances the effectiveness of TMS but also reduces the potential for systemic side effects that can accompany pharmacological interventions. Unlike medications that circulate throughout the body, potentially impacting organs and systems beyond the brain, TMS confines its effects primarily to the targeted brain regions, promoting a more focused and well-tolerated treatment approach.
Furthermore, the side effects associated with TMS are typically mild and transient, further emphasizing its safety and tolerability. Among the most common side effects reported by patients undergoing TMS treatment are mild headaches or scalp discomfort. Fortunately, these discomforts are generally short-lived, often resolving swiftly following the completion of a treatment session. This rapid resolution underscores the transient nature of these side effects and highlights TMS as a well-tolerated therapeutic option for managing ADD symptoms.
Overall, the exceptional safety profile of TMS makes it an attractive alternative for individuals seeking effective ADD treatment with minimized risk of systemic side effects. By prioritizing precision and patient comfort, TMS offers a reassuring option for those exploring alternative approaches to managing their ADD symptoms.
Considerations and Limitations
Although Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS) holds promise as an alternative treatment for Attention Deficit Disorder (ADD), it’s crucial to consider various factors before pursuing this option. One significant consideration is the cost of TMS therapy, which may pose a barrier for some individuals, especially since it is often not covered by insurance plans. The out-of-pocket expenses associated with TMS sessions can be prohibitive, limiting accessibility for those with financial constraints.
Furthermore, the optimal treatment protocol for TMS in managing ADD is still undergoing refinement. Questions persist regarding the ideal number and frequency of TMS sessions necessary to achieve optimal results. While existing research provides valuable insights, further exploration is needed to establish standardized guidelines for TMS treatment in ADD management.
Additionally, while short-term improvements in ADD symptoms have been observed following TMS therapy, the long-term effects remain uncertain. Extensive research is required to elucidate the sustained benefits and potential risks associated with prolonged TMS treatment. Moreover, identifying which subtypes of ADD are most responsive to TMS intervention is crucial for optimizing treatment outcomes. Tailoring TMS protocols to specific ADD profiles could enhance efficacy and ensure that individuals receive the most appropriate and beneficial treatment.
Summing Up
In conclusion, Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation presents a promising avenue for individuals seeking alternative treatments for ADD. Its targeted approach and minimal side effects make it an attractive option for those wary of traditional medications. However, more extensive research is necessary to fully understand its efficacy, optimal usage, and long-term effects. For now, individuals considering TMS for ADD should consult with a qualified healthcare provider to assess its suitability and explore other treatment options. As the field of neuromodulation continues to evolve, TMS holds the potential to revolutionize the management of ADD and improve the lives of those affected by this condition.