Ever wondered how the Earth’s rotation and tilt affect our seasons? The daily cycle of day and night and the yearly changes in sunlight and temperature shape our environment. By understanding the Earth’s orbit and axial tilt, you can learn more about each season’s unique traits.
Earth’s Rotation and Seasons
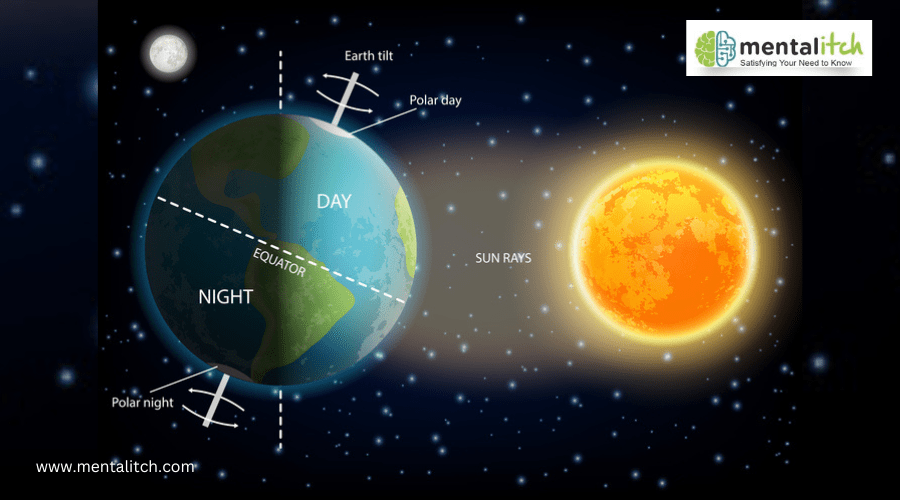
The Earth’s rotation on its axis takes about 24 hours and causes the day and night cycle. This rotation makes the sun rise in the morning and set in the evening, setting our daily rhythm.
The Earth’s tilt and orbit around the sun significantly impact our environment. The Earth is tilted at about 23.5 degrees relative to its orbital plane, which creates the seasons. As the Earth orbits the sun, different regions receive varying amounts of sunlight, leading to seasonal changes.
When the northern hemisphere tilts toward the sun, it experiences summer with longer days and shorter nights. Conversely, winter arrives with shorter days and longer nights when it tilts away. The summer solstice around June 21st marks the year’s longest day, while the winter solstice around December 21st marks the shortest day and the start of winter.
Spring Characteristics
As winter fades, spring brings a vibrant rebirth with blooming flowers and budding trees. Plants awaken from dormancy, and animals come out of hibernation.
Milder temperatures and longer daylight hours create an ideal environment for this season. The warmth and increased sunlight help plants flourish, and frequent rain showers provide essential water for new vegetation.
For farmers and gardeners, spring is a busy time for planting crops and tending to gardens. Favorable conditions allow seeds to germinate and plants to establish strong roots.
Summer Characteristics
Summer brings longer days and shorter nights, inviting everyone to enjoy the warmth and sunshine. The Earth’s tilt towards the sun provides extended daylight, making it perfect for outdoor activities like beach trips, swimming, and barbecues. The warm weather helps crops reach their peak.
Summer’s heat also triggers frequent thunderstorms. Warm air rises, causing atmospheric instability that leads to sudden, dramatic storms. These storms often provide welcome relief from the heat, bringing cooler air.
In many places, summer means vacations and festivals. Schools close, allowing families to travel and create lasting memories. Festivals celebrate everything from music to food, filling communities with vibrant energy. People take full advantage of the sunny weather to relax and have fun.
Autumn Characteristics
After the vibrant energy of summer, autumn brings cooler temperatures and shorter days. The air becomes crisper, and the sun sets earlier, marking the transition from summer warmth to winter chill.
One of the most striking features of autumn is the changing colors of leaves. Deciduous trees transform their foliage into brilliant shades of red, orange, and yellow as they prepare for the dormant winter months.
Animals sense this change and store food, migrate to warmer climates, or adapt their behaviors to survive the colder months.
Harvest festivals celebrate the bounty of crops like pumpkins, apples, and corn, offering a way to gather and enjoy the fruits of the growing season before winter.
Here are three key characteristics of autumn:
- Cooler Temperatures: The heat of summer subsides as temperatures drop.
- Changing Leaves: Trees put on a spectacular display of color.
- Harvest Time: Seasonal produce is abundant, and various harvest festivals take place.
Winter Characteristics
During winter, snow and ice transform the landscape into a frosty wonderland. The days are shorter, and the nights are longer. The cold temperatures and icy conditions present unique challenges for both nature and wildlife.
Animals adapt to the cold in various ways. Some hibernate, entering a state of deep sleep to conserve energy until warmer weather returns. Others grow thicker coats to insulate against the biting chill, while many birds and other creatures migrate to warmer regions to escape the harsh conditions.
Plants also exhibit amazing adaptability. Deciduous trees shed their leaves to conserve water and energy, while evergreens retain their needles, allowing them to continue photosynthesis even in the cold. Snow acts as a protective blanket for some plants, insulating them from extreme temperatures.
Snow and Ice Patterns
Winter brings a captivating array of snow and ice patterns shaped by temperature, precipitation, and wind.
Snowflakes are unique due to the molecular structure of water molecules, forming intricate designs when temperatures drop. Ice on bodies of water also forms distinct patterns, influenced by freezing temperatures and water currents, resulting in smooth or rough, cracked surfaces.
Winter’s artistry is evident in natural formations like icicles and frost on windows. Understanding these patterns is crucial for safety and winter sports activities.
Here are three interesting phenomena to observe:
- Snowflakes: Unique designs reflecting the conditions in which they were formed.
- Icicles: Created by dripping water that refreezes.
- Frost: Patterns on windows that resemble tiny forests.
Cold Weather Adaptations
Admiring winter’s intricate snow and ice patterns reveals how animals and plants adapt to survive the biting cold. Animals in frosty climates often develop thick fur or feathers for insulation. Some, like bears, hibernate to conserve energy and avoid the worst of the cold.
Plants have their strategies: many go dormant, pausing growth to save energy, while others shed leaves to reduce damage from freezing temperatures. This dormancy helps them survive until warmer months return.
Cold-blooded animals face unique challenges. Reptiles and amphibians might burrow underground to find stable temperatures, entering hibernation to conserve energy and avoid freezing.
Insects also have fascinating adaptations. Some produce antifreeze proteins to prevent ice formation in their bodies, while others burrow into the ground or find sheltered spots to wait out the winter. These strategies highlight the incredible resilience and adaptability of living organisms facing extreme cold.
Seasonal Activities
Engaging in seasonal activities makes each time of the year uniquely enjoyable. In spring, people can enjoy gardening. Summer calls for swimming at the beach, in a lake, or in a pool. Fall brings apple picking, a chance to enjoy the crisp air and scenic orchards. Winter offers skiing and snowboarding, perfect for embracing the cold and enjoying the snow.
Many cultural festivals and holidays align with these activities. Thanksgiving in the fall is synonymous with harvest and gratitude, while Christmas in the winter is celebrated with festive decorations and traditions. Your location also shapes your seasonal activities: coastal regions offer beach fun in the summer, while colder areas boast snow-related adventures in the winter.
Outdoor sports and recreational activities are best enjoyed in their respective seasons. Spring is ideal for hiking, allowing you to explore nature. Winter’s ice skating brings joy to frozen ponds and rinks. Traditional activities, like making snowmen in winter or attending vibrant spring festivals, add a sense of continuity and tradition to your seasonal enjoyment.
Adapting to Weather Changes
Staying prepared for weather changes is crucial as you engage in seasonal activities. Understanding seasonal weather patterns helps you manage temperature fluctuations and precipitation changes.
Here are some practical steps to ensure you’re ready for any weather:
- Dress in Layers: Wear layered clothing to adjust as temperatures change. Light, breathable layers work well in summer, while insulated layers are essential for colder months. Always have rain gear handy for unexpected showers.
- Monitor Weather Forecasts: Regularly check weather forecasts to plan outdoor activities and travel schedules effectively. Smartphone apps provide real-time updates to ensure you’re never caught off guard.
- Prepare Your Home: Implement energy-efficient practices and weatherproof your home. Seal windows and doors to keep out drafts, and maintain heating and cooling systems.
Develop emergency plans and stock up on essential supplies like food and water to be ready for unexpected weather events.
Conclusion
Understanding the Earth’s rotation and tilt reveals how they shape our seasons, influencing daily and yearly changes in sunlight and temperature. Each season offers unique traits and activities, from spring’s blooms to winter’s frosty landscapes. Animals and plants adapt with strategies like hibernation, dormancy, and migration.
Seasonal activities like gardening, swimming, apple picking, and skiing enhance our connection to nature and are celebrated through cultural festivals and holidays.