Studying ancient human settlements is like unlocking the secrets of our past. It helps us understand how people lived, worked, and created communities thousands of years ago. A “settlement” is a place where people have lived and left behind traces of their lives, like houses, tools, and pottery. In archaeology, these old settlements are like open books, telling us stories about our ancestors. By exploring these places, we learn not just about history, but also about how human societies have evolved over time. It’s a fascinating journey into the world of our forebears.
But the main question is, how would you determine the age of a certain settlement? Let’s discuss it first.
Criteria for Determining Age
Carbon Dating
To figure out how old an ancient settlement is, scientists use different methods. One popular method is carbon dating. This technique looks at the amount of carbon-14 in organic materials like wood or bones. Since carbon-14 decays over time, scientists can estimate how old something is based on how much is left.
Carbon dating is a clever way to find out how old something is. Imagine every living thing has a special clock inside it, made of a substance called carbon-14. While something is alive, this clock ticks steadily. But when it dies, the clock starts to slow down. By measuring how much the clock has slowed, scientists can tell how long ago the thing died. It’s a bit like checking how long a candle has been burning by seeing how much wax is left.
But carbon dating isn’t perfect. It works best for things that are up to about 50,000 years old. After that, there’s not enough carbon-14 left to get a good reading. And sometimes, the environment or other factors can mess with the results. Despite these challenges, carbon dating is a powerful tool for uncovering the secrets of the past. It helps us understand ancient life and how our world has changed over time.
stratigraphy
Stratigraphy is a way to understand Earth’s history by studying layers of rocks and soil. It’s like reading a book where each layer is a page from the past. The rule is simple: the lower the layer, the older it is. This helps scientists figure out the order of events over time.
In archaeology, stratigraphy helps us learn about ancient people and their lives. Each layer can hold artifacts, like tools or pottery, that tell us about different times. But it’s not always easy. Sometimes, layers get mixed up because of natural events or human actions. Despite this, stratigraphy is a key tool in piecing together the story of our planet and our ancestors.
Dendrochronology
Dendrochronology is a scientific method that uses tree rings to date events and changes in the environment. Each ring on a tree represents one year of growth, so by counting the rings, scientists can tell how old a tree is. But it’s not just about counting rings. The width and pattern of the rings can also give clues about the climate and conditions in which the tree grew. For example, a wide ring might mean a year with lots of rain, while a narrow ring could indicate a drought.
This method is especially useful in archaeology and historical research. By studying the rings in old wooden structures or artifacts, scientists can figure out when they were made. Dendrochronology can also help match up different pieces of wood from the same time period, creating a timeline of events. It’s like putting together a puzzle from the past, using the natural record keepers of the world – trees.
Oldest Human Settlements
Jericho, West Bank
Jericho is one of the oldest inhabited cities in the world, with evidence of settlement dating back to around 9000 BC. Located in the West Bank, near the Jordan River, it has been a continuous site of human habitation for over 11,000 years. Jericho is famous for its ancient walls, which are among the earliest examples of fortifications in human history. These walls, along with a stone tower, suggest that the inhabitants of Jericho were already practicing some form of urban planning and defense in the Neolithic period.
The city’s strategic location near a natural spring made it an important center for trade and agriculture. Over the centuries, Jericho has been inhabited by various cultures and civilizations, including the Canaanites, Israelites, and Romans. Archaeological excavations have uncovered a wealth of artifacts and structures, providing valuable insights into the daily life, technology, and architecture of its ancient residents.
Çatalhöyük, Turkey
Çatalhöyük is a remarkable Neolithic site located in the southern part of Turkey. Dating back to around 7500 BC, it is one of the best-preserved and most extensively studied prehistoric settlements. This ancient city is famous for its unique layout, with houses built so close together that they shared walls and had no streets in between. Residents entered their homes through openings in the roof, which also served as windows and chimneys.
The site is significant for its insights into early urban living, social organization, and cultural practices. The people of Çatalhöyük lived in a highly organized community, with evidence of specialized crafts, trade, and possibly even some form of proto-religion. The walls of the houses were adorned with elaborate frescoes, depicting hunting scenes, geometric patterns, and what are believed to be religious symbols. Burials were often done within the homes, with bodies buried under the floors, suggesting a strong connection between the living and their ancestors.
Mehrgarh, Pakistan
Mehrgarh is an important archaeological site located in the Balochistan province of Pakistan. It dates back to around 7000 BC, making it one of the earliest farming settlements in South Asia. The site is situated near the Bolan Pass, a crucial route connecting the Iranian Plateau to the Indus Valley, which played a significant role in the development and spread of early human civilizations.
Mehrgarh provides crucial evidence of the transition from hunting-gathering to farming and animal husbandry. The early inhabitants of Mehrgarh cultivated wheat and barley and domesticated animals such as sheep, goats, and cattle. This shift towards a more settled lifestyle led to the development of permanent structures, pottery, and more complex social structures.
The site is also notable for its continuous occupation through various phases of the Neolithic, Chalcolithic, and Bronze Age, showing the evolution of human societies over thousands of years. The gradual advancements in technology, architecture, and crafts such as bead-making and metallurgy at Mehrgarh reflect the increasing complexity of human societies.
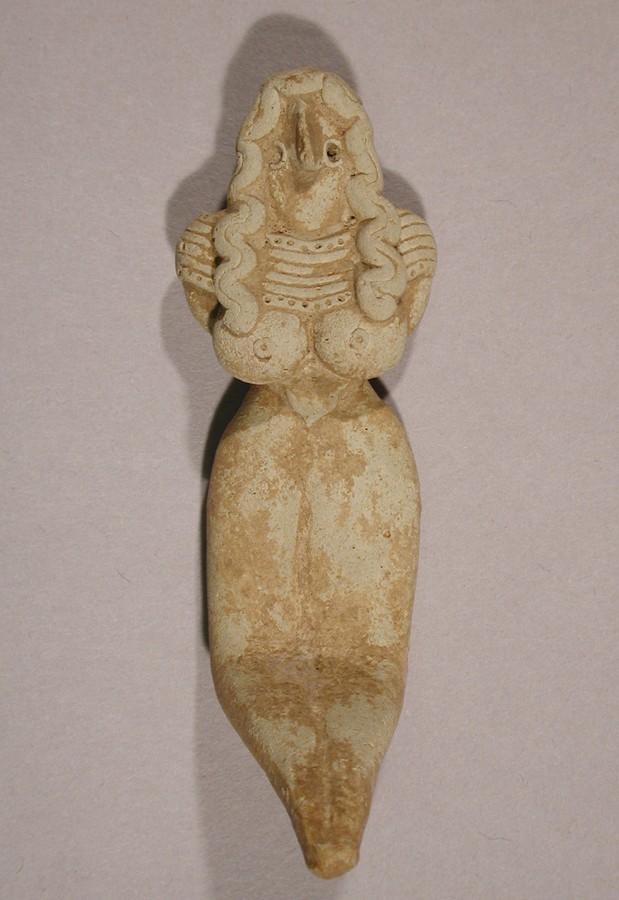
Ain Ghazal, Jordan
Ain Ghazal is a significant archaeological site located near Amman, the capital of Jordan. It dates back to around 7250 BC and is one of the largest and earliest Neolithic settlements in the Near East. The site covers an area of about 30 acres and was discovered in 1974 during road construction. Excavations have revealed a wealth of information about early human settlements in the region.
One of the most remarkable findings at Ain Ghazal is a collection of plaster statues and figurines. These statues are among the oldest large-scale human figures ever found and provide insights into the ritual and artistic practices of the time. The site also contains evidence of early architecture, including round and rectangular houses made of mud-brick walls and lime-plastered floors.
Ain Ghazal’s inhabitants practiced a mixed economy of hunting, gathering, and farming, with evidence of domesticated plants and animals. The site also shows signs of social organization and possibly early forms of governance. The archaeological findings at Ain Ghazal have greatly contributed to our understanding of the transition from nomadic lifestyles to more settled communities and the development of early human societies in the Near East.
Göbekli Tepe, Turkey
Göbekli Tepe is a fascinating archaeological site located in southeastern Turkey, near the city of Şanlıurfa. It dates back to around 9600 BC, making it one of the oldest known temples in the world. The site was first discovered in 1963, but its significance was not fully understood until excavations began in the 1990s under the direction of German archaeologist Klaus Schmidt.
Göbekli Tepe is composed of several large circular and oval-shaped stone structures, which are adorned with intricate carvings of animals and abstract symbols. These structures are believed to be ceremonial or religious in nature, suggesting that they were used for rituals or gatherings. The site’s massive T-shaped pillars, some of which weigh up to 20 tons, indicate a high level of sophistication in construction techniques for the time.
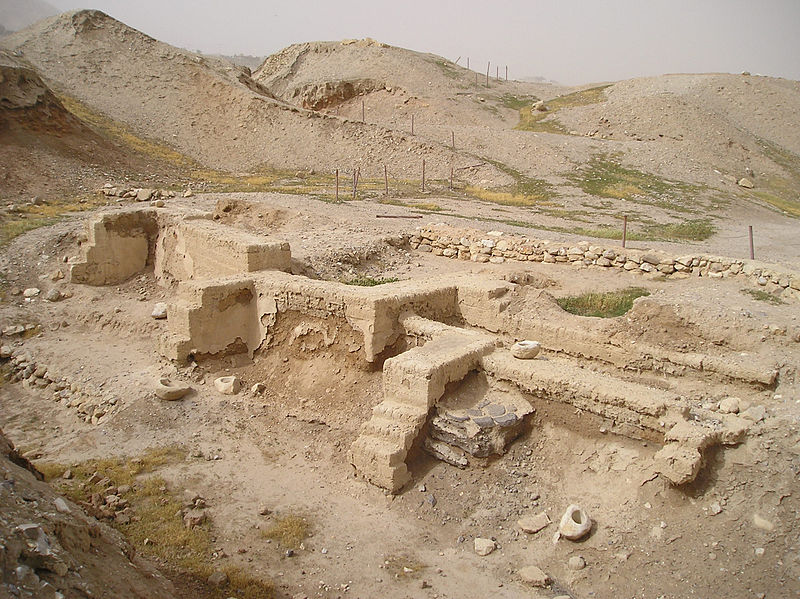
Tell Brak, Syria
Tell Brak is a significant archaeological site located in northeastern Syria, in the fertile region of ancient Mesopotamia. The site has a long history of occupation, dating back to at least 6000 BC, and was an important urban center during the early periods of Mesopotamian civilization.
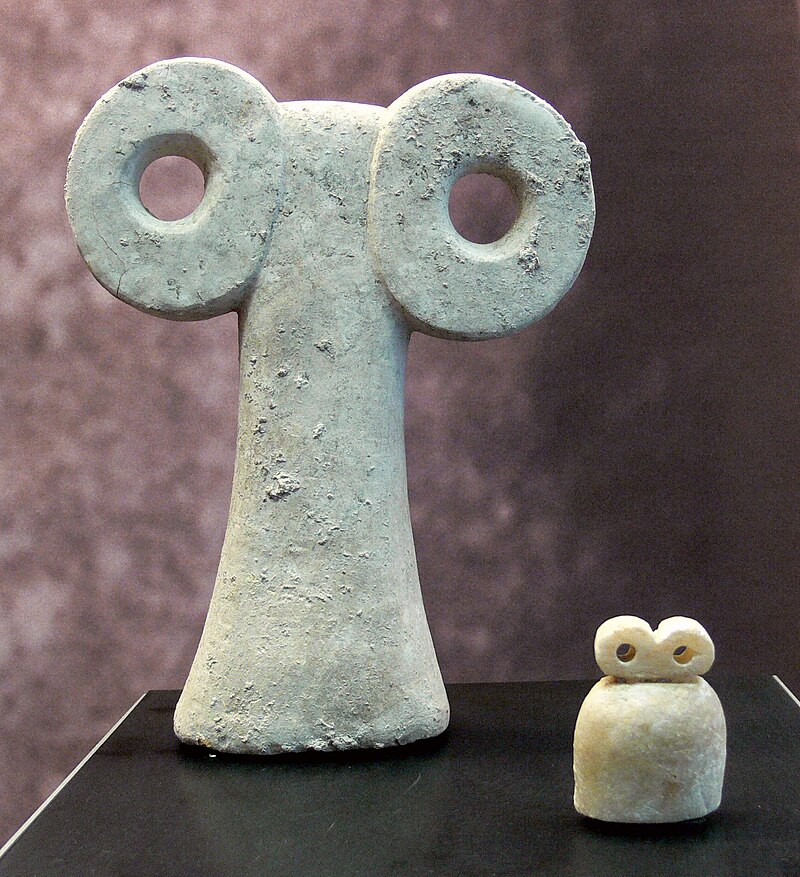
One of the key features of Tell Brak is its massive size, covering over 100 hectares at its peak. This suggests that it was one of the largest settlements in the region during the fourth and third millennia BC. Excavations at the site have revealed a complex urban layout, including a central mound surrounded by lower town areas. The presence of monumental buildings, such as the so-called “Eye Temple,” indicates the existence of religious and administrative structures.
The significance of Tell Brak lies in its role in understanding the development of urbanization in ancient Mesopotamia. The site provides evidence of early city planning, social organization, and long-distance trade networks. Additionally, the discovery of a large number of seal impressions and administrative tablets suggests that Tell Brak was an important administrative and economic center. Studying Tell Brak helps archaeologists and historians unravel the complexities of early urban societies and their interactions in the cradle of civilization.
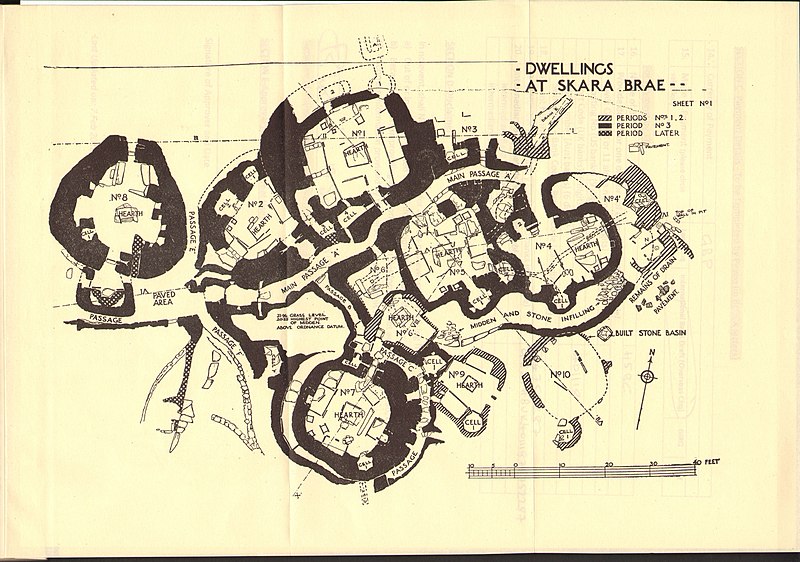
Skara Brae, Scotland
Skara Brae is a well-preserved Neolithic settlement located on the west coast of Mainland, the largest island in the Orkney archipelago of Scotland. It dates back to around 3180 BC and was discovered in 1850 after a storm uncovered part of the site. Skara Brae is remarkable for its preservation, providing a unique glimpse into the daily life of a prehistoric community.
The settlement consists of eight stone-built houses, connected by a series of low, covered passageways. Each house contains stone furniture, including beds, dressers, and hearths, which gives us a clear picture of Neolithic domestic life. The use of stone, rather than wood, for construction has ensured the survival of these structures for over 5,000 years.
Skara Brae is significant for understanding Neolithic life in Europe because it offers a rare, complete view of a prehistoric village. The level of preservation and detail provides insights into the social and economic organization of the community, their living conditions, and their interactions with the environment.
Conclusion
Exploring the oldest human settlements offers a fascinating window into the dawn of civilization. These ancient sites provide valuable insights into the lives of our ancestors, their cultural practices, and the evolution of human societies. By studying these settlements, we gain a deeper understanding of how early communities adapted to their environments, developed technologies, and formed social structures. Each site, with its unique features and artifacts, adds a piece of the puzzle to our collective history.