In the realms of design, animation, and technology, the terms “2D” and “3D” are thrown around quite frequently. While the difference might seem straightforward at first glance, there’s more complexity to these concepts than meets the eye. If you find yourself puzzled about these terms, rest assured, you’re not alone. Let’s dive into the fascinating world of 2D and 3D, breaking down their definitions and exploring their diverse applications in our daily lives.
Ask a professional if you need to learn more about 3d animation software.
The Definitions: 2D vs. 3D
Understanding the basic definitions is the first step in grasping the broader concepts.
-
2D (Two-Dimensional)
- Flat Surface Representation: 2D objects are defined on a flat plane, consisting of length and height but lacking depth. They are limited to two dimensions and do not have any thickness.
- Examples in Everyday Life: Drawings on paper, images on your computer screen, or the design on a piece of fabric are all 2D. They can be easily represented on a flat surface without any illusion of depth.
- Mathematical Perspective: In mathematics, 2D shapes are plotted on a Cartesian coordinate system along the X (horizontal) and Y (vertical) axes. These shapes can be measured in terms of area but do not have volume.
3D (Three-Dimensional)
- Occupying Space: Unlike 2D, 3D objects have depth in addition to length and height. This third dimension allows them to occupy space and be viewed from different angles.
- Real-World Examples: Anything that exists in the physical world and can be touched or held is 3D. From the furniture in your room to the trees in a park, these objects have a form and structure with measurable volume.
- Mathematical and Physical Aspects: In a mathematical context, 3D shapes are plotted on three axes – the X, Y, and the additional Z-axis, which represents depth or thickness. In physics, this concept is crucial for understanding the real-world structure and dynamics of objects.
Aspects of 2D and 3D Shapes
Understanding the aspects of 2D and 3D shapes is essential in fields ranging from geometry and art to engineering and virtual design. Let’s delve deeper into their characteristics and how they differ from each other.
Aspects of 2D Shapes
- Flat and Plane Surfaces: 2D shapes are flat. They exist solely on a plane, typically represented on paper, screens, or other flat surfaces. They have length and height but no depth.
- Measurement Aspects: These shapes are measured in terms of area, which is calculated using their length and height. Common measurements include square inches, square feet, or square meters, depending on the shape.
- No Volume or Thickness: Since 2D shapes lack a third dimension, they have no volume or thickness. This makes them ideal for graphical representations, designs, and illustrations where depth is not required.
- Examples in Geometry: Common 2D shapes in geometry include squares, rectangles, triangles, circles, and polygons. Each of these shapes follows specific rules regarding their angles and side lengths.
Aspects of 3D Shapes
- Occupying Space: 3D shapes have depth in addition to length and height, allowing them to occupy space. This depth gives them volume, making them tangible and relatable in the physical world.
- Measurement Complexity: 3D shapes are measured not only by area but also by volume, which involves length, width (or breadth), and height. Calculations for volume differ from shape to shape, reflecting their unique three-dimensional aspects.
- Real-World Interaction: Unlike 2D shapes, 3D shapes can be interacted with in a physical sense. This aspect is crucial in architecture, sculpture, product design, and other fields where spatial understanding is key.
- Variety of Forms: 3D shapes include prisms, cubes, spheres, cylinders, pyramids, and more complex polyhedra. Each of these shapes has distinct properties, like faces, edges, and vertices, which define their structure and appearance.
Visualization and Representation
- Visual Perception of 2D: 2D shapes are perceived exactly as they are represented, without any illusion of depth. Their simplicity makes them easy to draw and visualize but limits their representation of real-world objects.
- 3D Shapes and Depth Perception: 3D shapes provide a more realistic representation due to their depth. They can be viewed and understood from multiple angles, offering a comprehensive understanding of their structure.
Applications in Practical Fields
- 2D in Practical Applications: 2D shapes are widely used in graphic design, technical drawings, blueprints, and maps. They provide a clear and straightforward representation without the complexity of depth.
- 3D in Real-World Applications: 3D shapes are essential in fields requiring a realistic representation of space and form, such as architecture, engineering, and 3D modeling. They allow for a detailed understanding of an object’s or structure’s physical presence.
Practical Examples
To further illustrate the concepts of 2D and 3D shapes, let’s explore some practical examples from everyday life and various professional fields. These examples demonstrate how these shapes are not just theoretical constructs but are integral to our daily experiences and professional practices.
Everyday Life Examples
2D Shapes
- Graphic Design: In graphic design, logos, icons, and illustrations are typically 2D, lying flat on a surface like a webpage or a poster.
- Floor Plans: Architectural floor plans are 2D representations showing the layout of rooms in a building from a bird’s-eye view.
- Road Signs: Most road signs are 2D shapes, with symbols and text providing information in a clear, flat format.
3D Shapes
- Furniture: Objects like chairs, tables, and lamps in our homes are 3D, occupying space with their length, width, and height.
- Containers: Everyday items like boxes, bottles, and cans are 3D, holding volume and existing in three-dimensional space.
- Toys: Many children’s toys, such as building blocks or dolls, are 3D, offering tactile engagement in a physical space.
Professional Field Examples
2D Shapes in Professional Use
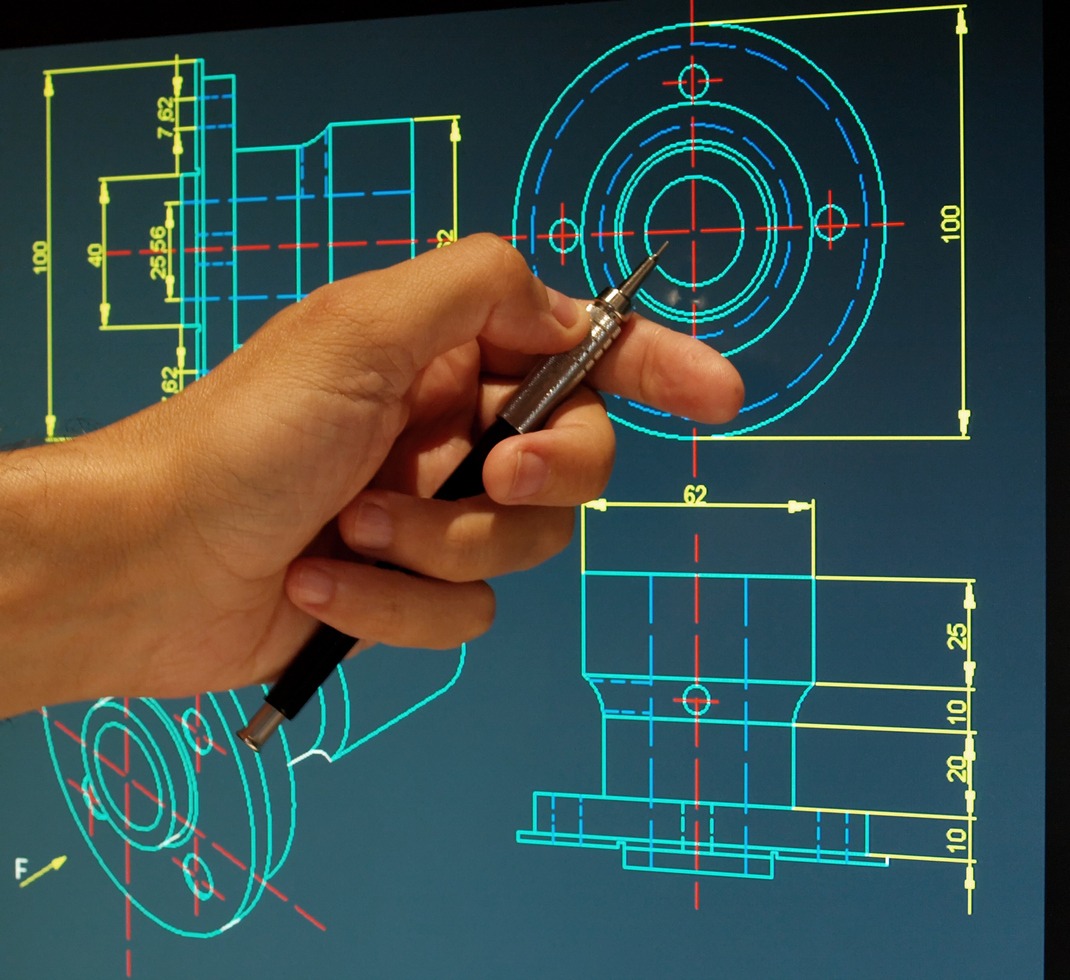
- Technical Drawing: Engineers and architects use 2D drawings to detail components of machinery or parts of buildings, focusing on dimensions and relationships without the need for depth.
- Fashion Design: Fashion designers often start with 2D sketches to conceptualize clothing before creating the actual 3D garment.
3D Shapes in Professional Use
- Product Design: Designing objects like smartphones, cars, or kitchen appliances involves 3D modeling to visualize the product’s appearance from all angles.
- Civil Engineering: Civil engineers use 3D models to visualize bridges, dams, and buildings, understanding their structure in the context of a real-world environment.
Mathematical and Educational Examples
2D Shapes
- Geometry Education: In school, students often begin geometry by learning about 2D shapes like triangles, squares, and circles, understanding their properties on a flat plane.
- Cartography: Maps are 2D representations of geographical areas, displaying locations and landscapes on a flat surface for easy interpretation.
3D Shapes
- Mathematical 3D Models: In higher education, students explore 3D shapes like cones, spheres, and cylinders, often using models or 3D diagrams to understand volume and surface area.
- Scientific Visualization: In fields like chemistry or biology, 3D models are used to represent molecules or anatomical structures, providing a realistic view of complex entities.
Art and Recreation Examples
2D Shapes
- Paintings and Drawings: Traditional art forms like paintings and drawings use 2D shapes and lines to create images on canvas or paper.
- Board Games: Many board games are played on a 2D surface, with game elements like cards and boards designed in two dimensions.
3D Shapes
- Sculpture: Sculptors create 3D art, giving their creations form and volume that can be appreciated from different angles.
- Virtual Reality: VR experiences are based on 3D environments, immersing users in a simulated space that feels more realistic due to its three-dimensional nature.
Applications in Various Fields
he use of 2D and 3D shapes extends across various fields, each harnessing these dimensions in unique and innovative ways. Let’s explore how both 2D and 3D shapes are applied in different professional and practical areas.
Applications of 2D Shapes
- Graphic Design and Art:
- Print Media: In magazines, brochures, and billboards, 2D designs are used to convey messages and information visually.
- Digital Art: Artists create 2D digital art for various purposes, from web design to digital advertising.
- Cartography:
- Map Making: Maps are 2D representations of the world, providing navigational information in a flat, easy-to-read format.
- Architecture and Engineering:
- Blueprints and Floor Plans: These are typically 2D representations showing the layout and design of buildings and structures.
- Education:
- Teaching Tools: 2D shapes are used in educational materials, like geometry textbooks, to teach various concepts.
- Fashion Design:
- Initial Sketches: Designers use 2D sketches to conceptualize clothing before turning them into 3D garments.
Applications of 3D Shapes
- Architecture and Construction:
- Building Models: 3D models are used to visualize and plan buildings before they are constructed.
- Interior Design: 3D modeling helps in visualizing and planning interior spaces.
- Film and Animation:
- 3D Animation: Modern animation heavily relies on 3D modeling to create lifelike and dynamic characters and scenes.
- Special Effects: Many special effects in movies are created using 3D technology.
- Gaming Industry:
- Game Design: 3D models are essential in creating immersive and interactive gaming environments.
- Manufacturing and Product Design:
- Prototyping: 3D shapes are used to create prototypes of various products, from household items to advanced technological devices.
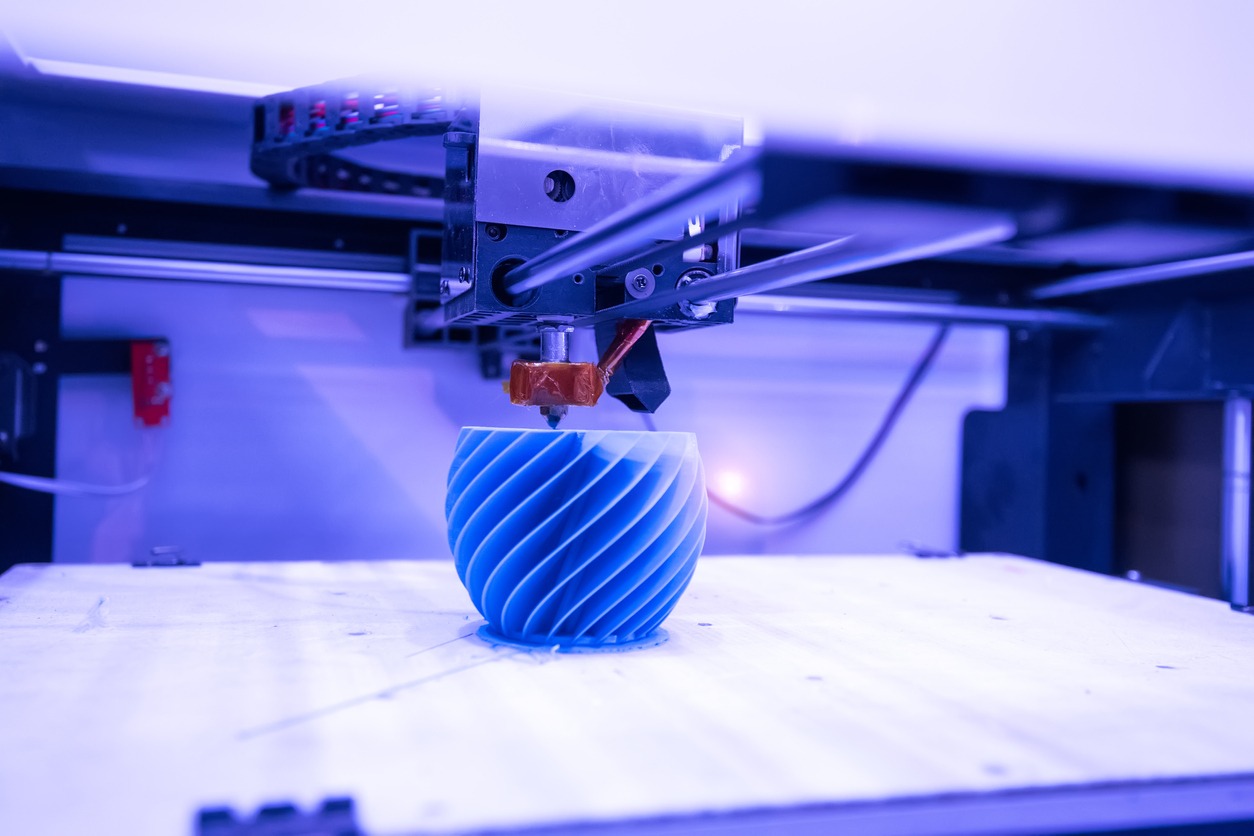
- 3D Printing: This technology uses 3D models to create physical objects layer by layer.
- Medical Field:
- Imaging and Simulation: 3D models are used in medical imaging (like MRI and CT scans) and for simulating surgical procedures.
- Prosthetics Design: 3D modeling helps in designing and creating customized prosthetics.
- Science and Research:
- Molecular Modeling: In chemistry and biology, 3D models represent molecular structures for better understanding and research.
- Astronomy and Space Exploration: 3D modeling is used to simulate celestial bodies and space missions.
- Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR):
- Immersive Experiences: VR and AR technologies use 3D environments to create immersive experiences for education, entertainment, and training simulations.
- 2D vs. 3D Scanning
-
- 2D Scanning: Introduced in the 1900s for scanning blueprints and documents, turning physical papers into digital formats.
- 3D Scanning: Breaks down real-world objects or environments into digital 3D designs or models, used extensively in engineering, industrial design, and manufacturing.
Wrapping Up: 2D and 3D in Our World
Understanding 2D and 3D goes beyond school lessons. It’s about applying these concepts in real-world scenarios, whether in designing, animating, or even using everyday technology. So next time you embark on a project, consider whether 2D or 3D suits your vision best.
Science and discovery is always fun and interesting but can be challenging! For more insights into the fascinating world of design and technology, keep exploring with us. Your next discovery is just a read away!